What is NFT Loans and how does it work

What are NFT loans?
NFT loans are becoming increasingly popular as NFTs can be used to replace physical items as collateral. These loans are offered by DeFi (Decentralised Finance) platforms and are meant to facilitate more efficient lending. Borrowers using NFTs as collateral means no need to use fiat currency every time they want to take a loan. Such a method is popular among borrowers and investors even when the market is crashing.
Why do we need NFT loans?
The short answer is that NFTs are relatively illiquid. You may have read somewhere that artists receive royalties for every secondary sale of their NFT on an NFT market platform. This is true. However, for the NFT to be sold at all, takes a long time. Many NFT platforms such as OpenSea and SuperRare have NFTs listed with various buyers’ bids for the item. As these NFTs are sold via auctions, it takes time before the cryptocurrency appears in the seller’s wallet. This lack of funds could hinder collectors from acquiring their desired NFTs. Using NFT loans can thus help them get around this issue.
How do NFT loans work?
For the most part, the basic concept of NFT loans is the same as that of a bank loan. A borrower will put up their assets as collateral and take a loan. The borrower will then have to repay this loan and the interest before the predetermined expiration date. Failure to do so will result in the borrower forfeiting the asset that they put up as collateral. There are 4 kinds of NFT loans, each of which will be explained below.
1. Peer-to-peer NFT lending
This kind of lending works on a typical market mechanism where lenders and borrowers are matched with one another. A user first lists their NFT on an NFT lending platform. They will then start to receive loan offers from others: meaning that there will be users willing to lend the borrower money. Once the borrower accepts an offer, they immediately receive WETH (wrapper ETH) from the lender’s wallet. the NFT that was offered as collateral will be transferred into a digital vault for the duration of the loan. This digital vault should be a part of the lending platform used.
An example of a lending platform is Digicol. Lending platforms such as Digicol allow platform users to either use their NFT as collateral or offer tokens to NFT holders. The image below provides an overview of the transaction mechanisms offered.
 Digicol’s collateral market mechanism
Digicol’s collateral market mechanismCollateral Market Mechanism chart
If the borrower repays the loan before the expiration date, they can get their NFT back into their wallet. However, if the borrower defaults on their loan before its expiration date, the lender will receive the borrower’s NFT from the decentralised vault at a huge discount. It should be noted here that the floor price of the NFTs does not influence the price at which this lender can buy the NFT. Its value is determined by the terms of the peer-to-peer lending contract.
2. Peer-to-protocol lending
For peer-to-protocol lending, the borrower borrows from a protocol itself. NFT Protocol is a decentralised trading infrastructure to support different NFT classes. Meaning that to borrow from the protocol, the borrower has to adhere to a fixed set of rules set beforehand. This mechanism involves the contributions from liquidity providers. These providers must first add their funds to a protocol pool. Borrowers who wish to access this liquidity must first collateralise their NFT. This NFT will then be locked up in the protocol’s digital vaults.
One platform that uses this lending mechanism is BendDAO. Whether or not an NFT gets liquidated is determined by a certain health factor. The higher the value of the health factor, the safer your NFT is from liquidation. To determine the amount at which the NFT is liquidated, lending platforms will take reference from major NFT trading platforms such as OpenSea to find out the floor price of these NFTs.
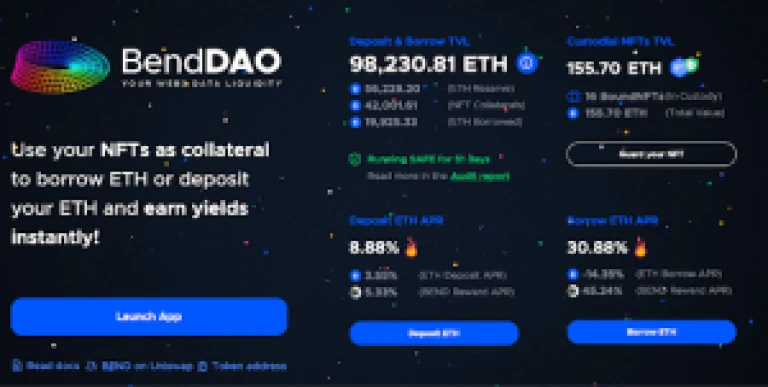 Screenshot showing how BendDAO works
Screenshot showing how BendDAO worksAnother way to make use of your NFTs in this way is to stake your NFT. By pooling your assets into a decentralised autonomous organisation, holders are often able to gain more access to governance tasks on the platform. Do check out our article on NFT Staking on Niftyzone!
3. Non-fungible debt positions
By using this method, users ‘exchange’ their NFTs for a synthetic stablecoin called $PUSd. This means that to gain access to the $PUSd, NFTs have to be used as collateral. This stablecoin is pegged to the USD on a 1:1 basis. Borrowers can use this stablecoin to provide liquidity on the protocol and earn interest to fund other transactions on the blockchain. $PUSd can also be swapped for other cryptocurrencies to seek opportunities elsewhere if the blockchain you are transacting on does not have what you want. Once the loan is repaid, NFT owners can have their NFTs back. Failure to do so will result in the NFT being liquidated.
4. NFT Rentals
This method is the only method out of the 4 which does not involve a digital vault. Instead, rental platforms such as reNFT match tenants to renters, with varying rental terms and conditions. This mechanism works in the same way that a peer-to-peer NFT lending transaction would work, but with a few extra benefits. For example, as a tenant of a rented NFT, one gets greater access to perks such as exclusive access to Discord servers. If you hold on to a certain NFT, you may also be shortlisted for giveaways.
Thanks for reading! At Niftyzone, we value your craft and wish to share it with the NFT Community!
Follow our Twitter and Telegram for more updates on our Marketplace.
Feel free to contact us for any further inquiries, or have a look at our FAQ page as well!









