Why is “Generative Art” a Game Changer in this Tech-driven World?

What is Generative Art, and why does it matter?
From digital compositions to mind-bending installations, this unique form of art generation is grabbing audiences across the globe. But what exactly is Generative Art? How did it come to be? And why does it matter in this current digital space?
What is Generative Art?
The word “Generative Art” was first coined in 1965 by the German philosopher “Max Bense ”. A form of generation, where they use algorithms, computer programs, mathematical formulas or other automated systems to generate artwork. Instead of relying solely on manual techniques, generative work makes use of technology to produce unique and ever-changing pieces.
At its core, generative art blurs that thin line between human work and AI. It embraces randomness, unpredictability, and emergence as its fundamental elements in the creation process.
The beauty of it lies in its ability to create infinite variations from a set of underlying rules or parameters. With each iteration or interaction, the artwork evolves organically and takes on a life of its own. This dynamic nature not only challenges our conventional notions of authorship but also invites viewers to engage with art in interesting ways.
Generative art can take many forms – from intricate digital graphics rendered by complex algorithms to physical installations that respond to real-time data inputs. The possibilities are virtually limitless! Users can experiment with colours, shapes, patterns, and movements.
The History of Generative Art
It’s a fascinating journey that spans several decades. It all began in the 1960s when artists and computer scientists started exploring the potential of computers to create artwork. These pioneers were intrigued by the idea of using algorithms and code to generate visual compositions.
One notable figure in this movement was Harold Cohen, who was a painter and an engineer. He developed an artificial intelligence program called AARON in the early 1970s. AARON was capable of creating original drawings, mimicking human artistic techniques through its algorithmic processes.
In the following years, advancements in technology allowed for more complex and intricate generative artworks to be created. Artists like Vera Molnar and Manfred Mohr embraced this new medium, pushing boundaries with their innovative use of algorithms.
Fast forward to today, and we see a resurgence of interest in generative art. With powerful computing capabilities and sophisticated software tools at our disposal, artists can explore endless possibilities for creating unique visuals.
It has become not just a form of creative expression but also a reflection of how technology impacts our lives.
Generative art matters because it expands our understanding of creativity while providing a glimpse into the future possibilities offered by emerging technologies.
Types of Generative Art
In the field of generative art, there are numerous types and each of those brings in a unique approach and techniques to the creation process, resulting in unique outcomes.
One prominent type is “Algorithmic Art“. This form relies on mathematical algorithms to dictate the creation process, allowing for intricate patterns, shapes, and colours to emerge. Artists can manipulate variables within the algorithm to produce endless variations and explore different aesthetic possibilities.
Another type is “Fractal Art“, which uses complex mathematical formulas to generate self-repeating patterns at various scales. These mesmerizing artworks often resemble intricate geometrical shapes found in nature, such as snowflakes or fern leaves.
“Evolutionary Art” takes inspiration from biological systems by implementing genetic algorithms. In this approach, artists create an initial set of digital organisms with specific traits or characteristics. Through iterations of selection and mutation processes, these organisms evolve into visually stunning compositions that mimic natural selection principles.
“Procedural Art” involves creating artwork through predefined rules or procedures rather than relying solely on human intervention. Artists design systems that generate visuals based on predetermined parameters or instructions. The beauty lies in the unexpected results that arise from these automated processes.
“Interactive Generative Art” allows viewers to actively engage with the artwork by influencing its evolution or transformation through input devices like sensors or touchscreens. This dynamic interaction between the audience and artwork creates an immersive experience where each person becomes a co-creator.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of generative art forms out there today.
Why does Generative Art matter?
Well, let’s get into the reasons why this innovative form of art has captured the attention and imagination of artists, collectors, and enthusiasts alike.
By using algorithms, randomization, or code to create artwork, artists can explore new possibilities that may have been unimaginable otherwise. This opens up a world of experimentation and innovation.
Unlike traditional artworks that are created by a single artist’s hand, generative art often involves collaboration between human creators and machines. This blurring of boundaries raises thought-provoking questions about originality and the role of technology.
Furthermore, generative art has also found its place in contemporary culture through its ability to reflect current societal trends and issues. Artists can use algorithms to generate artwork that responds to real-time data or social media feeds. This dynamic nature allows for an ongoing dialogue with audiences on relevant topics like climate change or social justice.
Moreover, generative art holds great potential for creating unique experiences for viewers. With interactive installations or virtual reality platforms incorporating generative elements into their design, spectators become active participants in shaping their encounters with the artwork.
Last, but not least, is how NFTs (non-fungible tokens) have revolutionized the market for digital artworks including generative creations. Through blockchain technology, artists can now authenticate their work as one-of-a-kind originals which holds tremendous value both aesthetically and monetarily. We will talk about this in the further section.
Generative Art matters because
- It challenges conventional norms
- It offers fresh perspectives on authorship
- Reflects contemporary issues
- Creates immersive experiences
- Finds new avenues for artist’s success through NFTs!
So next time you encounter a piece of computer-generated artwork- remember how far we’ve come in the field of art and technology advancement.
Real-world examples
DeepDream – A project developed by Google in 2015. DeepDream uses a convolutional neural network to enhance and transform images, creating surreal and dreamlike visuals.
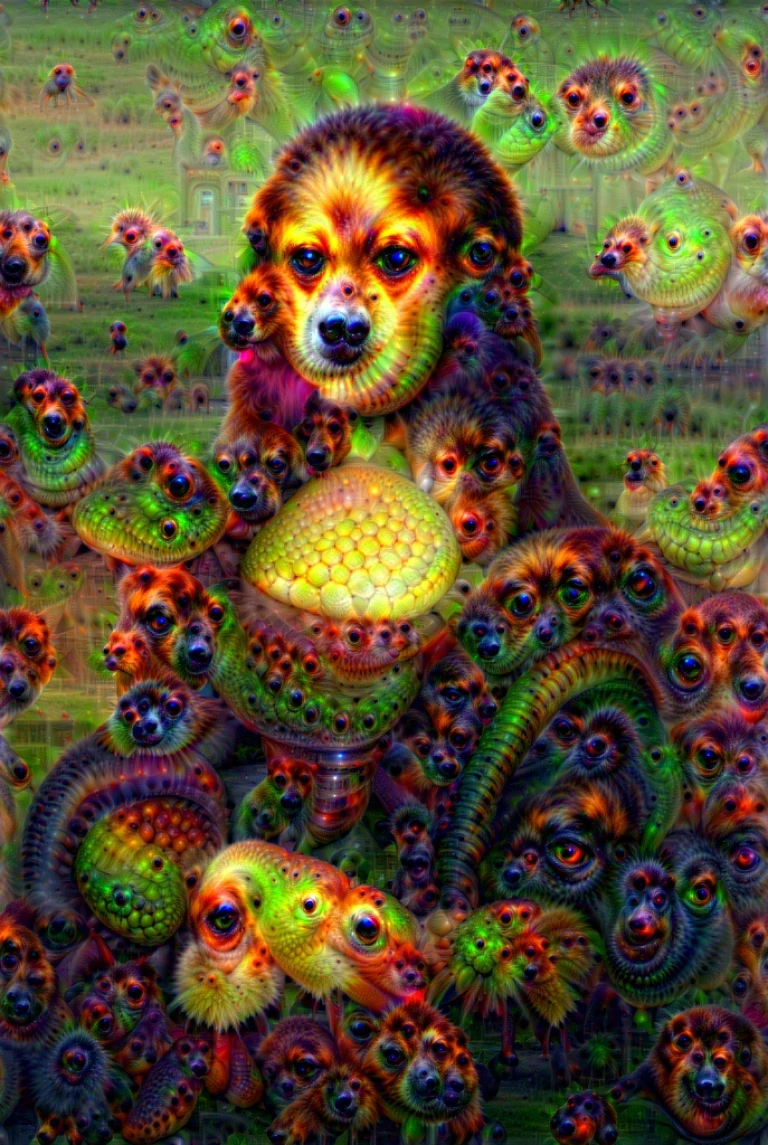 “Mona Lisa” with DeepDream effect using VGG16 network trained on ImageNet created by P.J. Finlay using code written by Aleksa Gordic.
“Mona Lisa” with DeepDream effect using VGG16 network trained on ImageNet created by P.J. Finlay using code written by Aleksa Gordic.Using machine learning algorithms, DeepDream can identify patterns in an image. It essentially allows us to see through the eyes of artificial intelligence.
This groundbreaking technology has been used in various artistic endeavours, from transforming ordinary photographs into psychedelic masterpieces to generating stunning animations.
Another real-world example that showcases the power and relevance of generative art is “The Next Rembrandt” project.
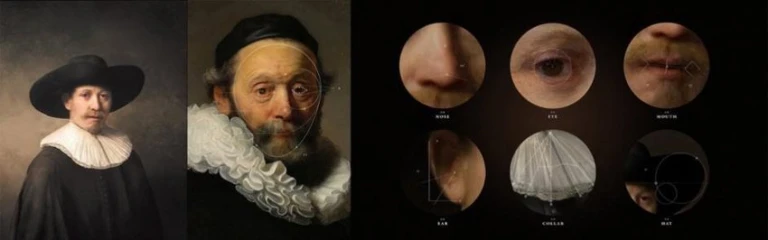 Source: ResearchGate (https://shorturl.at/jACIL)
Source: ResearchGate (https://shorturl.at/jACIL)Using machine learning algorithms trained on Rembrandt’s works, a team created an entirely new painting in his distinctive style. This project demonstrated how AI can be leveraged not just as a tool but as an active participant in the creative process.
The versatility of this real-world application speaks volumes about the potential impact of generative art on our society.
Generative art opens up new possibilities for artistic collaboration across different disciplines such as science, technology, mathematics, and design. With its ability to merge human creativity with advanced computational power, it has become a powerful medium for self-expression.
The relation between Generative Art and NFTs
The relationship between generative art and NFTs is a fascinating and symbiotic one. NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, have gained immense popularity in recent years as a way to tokenize and authenticate digital assets. These unique tokens are perfect for the world of generative art, which thrives on creating one-of-a-kind pieces using algorithms and computational processes.
NFTs provide a solution to the long-standing challenge of provenance in the digital art world. By attaching an NFT to a generative artwork, artists can establish ownership and ensure that their creations cannot be replicated or tampered with. This not only protects the value of the artwork but also gives artists greater control over their intellectual property.
Furthermore, NFTs enable artists to monetize their generative art in ways that were previously unimaginable. With traditional forms of art, such as paintings or sculptures, there’s often only one physical copy that can be sold. However, with generative art, multiple variations can be created from a single algorithmic process. Each variation can then be tokenized as an individual NFT and sold separately.
This opens up new avenues for both collectors and creators alike. Collectors can own unique pieces of generative art that evolve over time based on dynamic algorithms. Creators can generate ongoing revenue by selling limited editions or even allowing collectors to participate in the creative process by customizing certain parameters within the algorithm.
The relationship between generative art and NFTs is mutually beneficial – NFTs bring credibility and value to generative artworks while empowering artists with newfound opportunities for monetization.
Conclusion
Generative art has gradually evolved from its early roots in computer programming to the vast array of techniques and mediums used today.
The history of generative art tells a story of pioneering artists who embraced technology as a means to create unique, ever-evolving artworks. The use of algorithms, randomness, and interactivity sets this genre apart from other forms of visual art.
There are various types of generative art including fractals, algorithmic art, cellular automata, and procedural generation. Each offers a distinct style and approach but shares the common thread of utilizing computational power.
In conclusion, generative Art represents an exciting frontier where technology meets creativity.